Examples
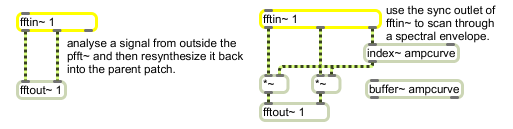
fftin~ outputs a frequency/domain signal pair and a sync signal that indicates the bin number
Input for a patcher loaded by pfft~
| Name | Type | Opt | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| inlet-assignment | int | Obligatory. Determines the inlet number of the pfft~ which will be routed into the fftin~ object. Inlet assignment starts at one, for the leftmost inlet in the pfft~. Multiple fftin~ objects will typically have different inlet numbers. | |
| window-envelope-function | symbol | Specifies the window envelope function the fftin~ object will apply to overlapping FFTs on the input signal. The options are (i.e. no window envelope), (the default), , and (Note: The Blackman window should be used with an overlap of 4 or more). If the symbol is used, then the fftin~ object will not use a windowing envelope and will not perform a Fast Fourier Transform -- it will echo the first half of its input sample window to its real output and the second half of its input sample window to its imaginary output. This can allow you to input raw control signals from outside the parent patcher through inlets in the pfft~ object, provided its overlap is set to 2. Other overlap values may not yield useful results. |
| signal | Dummy inlet for the connection of a begin~ object. The signal input for an fftin~ object is an inlet in the pfft~ subpatcher which contains the object. |

| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| cartopol | Cartesian to Polar coordinate conversion |
| cartopol~ | Signal Cartesian to Polar coordinate conversion |
| fft~ | Fast Fourier transform |
| fftinfo~ | Report information about a patcher loaded by pfft~ |
| fftout~ | Output for a patcher loaded by pfft~ |
| frameaccum~ | Compute "running phase" of successive phase deviation frames |
| framedelta~ | Compute phase deviation between successive FFT frames |
| ifft~ | Inverse fast Fourier transform |
| in | Message input for a patcher loaded by poly~ or pfft~ |
| out | Message output for a patcher loaded by poly~ or pfft~ |
| pfft~ | Spectral processing manager for patchers |
| poltocar | Polar to Cartesian coordinate conversion |
| poltocar~ | Signal Polar to Cartesian coordinate conversion |
| vectral~ | Vector-based envelope follower |
| MSP Tutorial 26: Frequency Domain Signal Processing with pfft~ | MSP Tutorial 26: Frequency Domain Signal Processing with pfft~ |