Examples
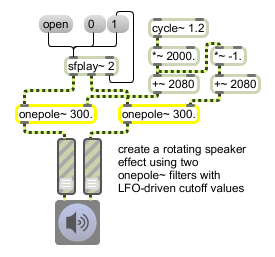
onepole~ provides efficient filtering for a simple sample player
Single-pole lowpass filter
| Name | Type | Opt | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| center-frequency (Hz) | float | opt | Sets the center frequency for the filter, as described above. |
| Hz/linear/radians | symbol | opt | Using the symbols , , or for an optional second argument sets the frequency input mode. The default mode is Hz (which is the same as providing no mode argument). Using the argument sets the frequency input mode to linear (0 - 1). Using the argument sets the frequency input mode to radians (0 - 1). |
| int | center-frequency (Hz) [int] |
Performs the same function as . |
| float | center-frequency (Hz or 0 through 1 specified by object-argument) [float] |
In right inlet: Sets the frequency for the filter (if no signal is connected). By default, frequency is expressed in Hz, where the allowable range is from 0 to one fourth of the current sampling rate. For convenience, onepole~ has two additional input modes that use the more conventional input range, 0 - 1 (see the and messages). |
| Hz | In either inlet: Sets the frequency input mode to Hz (the default). | |
| clear | In either inlet: Clears the internal state of onepole~. Since onepole~ does not have the inherent instability of other filter types, this should never be necessary. | |
| linear | In either inlet: Sets the frequency input mode to linear (0 - 1). Linear mode is simply a scaled version of the standard Hz mode, except that values in the 0-1 range traverses the full frequency range. | |
| radians | In either inlet: Sets the frequency input mode to radians (0 - 1). Radians mode lets you set the center frequency (cf) of the equation directly, while the input has the same range (0-1), the output has a curved frequency response that is closer to the exponential pitch scale of the human ear. | |
| signal | In left inlet: Signal to be filtered. In right inlet: A signal can be used to set the frequency for the filter, with the same effect as a float. If a signal is connected to this inlet, its value is sampled once every signal vector. |
