Examples
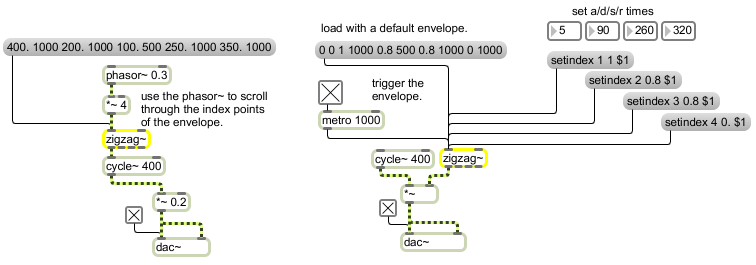
zigzag~ can be used as a multi-purpose editable ramp generator
Linked list function editor
| Name | Type | Opt | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| initial-target-value | int or float | opt | Sets an initial target-value (y) for the zigzag~ object. |
| bang | In left inlet: The zigzag~ object responds to a message according to its mode of behavior, which is set using the message. If the zigzag~ object is set to mode 0 or mode 1, a message will cause the zigzag~ object to go to the start point (or end point if the direction is negative) and begin outputting values from there. If the zigzag~ object is set to mode 2, a message will cause the zigzag~ object to jump to the next index in the list (or the previous index, if the current direction is negative) and begin outputting values from there. |
|
| int | output-rate-coefficient [int] |
In right inlet: Specifies the rate at which the value and time pairs will be output. A value of 1.0 traverses the list forward at normal speed. A playback rate of -1 traverses the list backwards (i.e. in reverse). A value of .5 traverses the linked list at half the normal speed (effectively doubling the delay time values). (In left inlet: Converted to float.) |
| float | output-rate-coefficient [float] |
In left inlet: Each element in the zigzag~ object's linked list is a pair that consists of a target value (y), followed by a second number that specifies a total amount of time in milliseconds (delta-x). In that amount of time, numbers are output regularly in a line from the current index value to the target value. The list describes a line which begins with a value of 0 at time 0, rises to a value of 3.5 a half second later, and rises again to a value of 10 in 1 second. In right inlet: Specifies the rate at which the value and time pairs will be output. A value of 1.0 traverses the list forward at normal speed. A playback rate of -1 traverses the list backwards (i.e. in reverse). A value of .5 traverses the linked list at half the normal speed (effectively doubling the delay time values). |
| list | position-index and event-pair [list] |
Performs the same function as (without the word, "append"). |
| append | position-index and event-pair [list] |
In left inlet: The word , followed by an which specifies a position (where 0 is the first element) and a list, will insert new event pair(s) after the index specified. The message will create a new second entry in the linked list (at the 0 index) with a value of 5 and a time of 500 milliseconds. |
| bangdelta | transition-time [float] |
In left inlet: The word , followed by a or , specifies the time over which the transition between values occurs when the zigzag~ object receives a . The default is 0 (i.e., and immediate transition). |
| bound | start-and-end-points [list] |
In left inlet: The word , followed by two numbers which specify start and end indices (where 0 is the first element), sets the start and end points of the zigzag~ object's linked list. |
| delete | position-index [list] |
In left inlet: The word , followed by an which specifies a position (where 0 is the first element), will delete the value and time pair associated with that index from the list. A can follow the message if you want to remove multiple event pairs from the list. The message will remove the current first value and time pair from the list; the second value and time pair (i.e. the value and time pair at index 1) will now become the first values in the list. |
| dump | In left inlet: The word will cause a list consisting of all currently stored value and time pairs in the form to be sent out the zigzag~ object's 3rd outlet. |
|
| end | ending-position-index [float] |
In left inlet: The word , followed by an which specifies a position (where 0 is the first element), sets the point at which the zigzag~ object ceases its output when triggered by a . |
| insert | position-index and event-pair [list] |
In left inlet: The word , followed by an which specifies a position (where 0 is the first element) and a list, will insert new event pair(s) before the index specified. The message will create a new first entry in the linked list (at the 0 index) with a value of 5 and a time of 500 milliseconds. |
| jump | position-index and transition-time [list] |
In left inlet: The word , followed by an which specifies a position (where 0 is the first element), skips to that point in the linked list and begins outputting value and time pairs from that point. An optional int can be used to specify the time, in milliseconds, over which the transition to the next value will occur (the default value is ). |
| jumpend | transition-time [float] |
In left inlet: The word causes the zigzag~ object to immediately jump forward to the last value (y)on the linked list. |
| jumpstart | transition-time [float] |
In left inlet: The word causes the zigzag~ object to immediately jump to the first value (y)on the linked list and then output the currently selected list or selected portion of the list. |
| mode | object-response-mode (0 through 3) [int] |
The word , followed by a number in the range 0-3, specifies the way that the zigzag~ object responds to messages and signal values. The modes of operation are: mode 0 is the default mode of operation. When the zigzag~ object receives a , it will jump to the start point (or end point if our direction is negative) and begin outputting values from there. The time value associated with this jump has its length defined by the message. The default value for is . If a signal is connected to the left inlet of the zigzag~ object in this mode, the current index of the list is determined by the signal; any previously set , , , and messages are ignored. mode 1 behavior for the zigzag~ object is exactly the same as in mode 0 in terms of the effect of a . In mode 1, signal inputs are handled differently. If a signal is connected to the left inlet of the zigzag~ object in mode 1, the input signal functions as a trigger signal; when the slope of the input signal changes from non-negative to negative, the object will be re-triggered as though a were received. mode 2 sets the zigzag~ object to jump to the next index in the list (or the previous index, if the current direction is negative) and begin outputting values from there. The time value associated with this jump has its length defined by the message. The default value for is . If a signal is connected to the left inlet of the zigzag~ object in mode 2, the input signal functions as a trigger signal; when the slope of the input signal changes from non-negative to negative, the object will be re-triggered as though a were received. |
| loopmode | looping-enable-flag (0 or 1) [int] |
The word , followed by 1, turns on looping. turns off looping. By default, looping is off. turns on looping in "pendulum" mode, in which the value and time pairs are traversed in an alternating forward and reverse direction. By default, looping is off |
| next | transition-time [float] |
In left inlet: The word skips to the next value and time pair in the linked list. An optional can be used to specify the time over which the transition to the next value will occur (the default value is ). |
| prev | transition-time [float] |
In left inlet: The word skips to the previous value and time pair in the linked list. An optional can be used to specify the time over which the transition to the previous value will occur (the default value is ). |
| In left inlet: The word causes the current status and contents of the zigzag~ object to be printed out in the Max window. The output consists of the current mode, loopmode, the start, end, and loop length of the current list, the pendulum state, and moving value of the object, followed by a listing of each index in the linked list, along with its y and delta-x values. | ||
| setindex | position-index target-value and transition-time [list] |
In left inlet: The word , followed by an which specifies a position (where 0 is the first element) and a pair of floats, sets the target value (y) and transition time amounts (delta-x) for the specified position in the list. |
| signal | In left inlet: The zigzag~ object responds to signal values according to its mode of behavior, which is set using the message. If the zigzag~ object is set to , the current index of the list is determined by the input signal value; any previously set , , , and messages will be ignored. If a signal is connected to the left inlet of the zigzag~ object in , the input signal functions as a trigger signal; when the slope of the input signal changes from non-negative to negative, the object will be re-triggered as though a were received. If a signal is connected to the left inlet of the zigzag~ object in , the input signal functions as a trigger signal; when the slope of the input signal changes from non-negative to negative, the object will be re-triggered as though a were received. In right inlet: A signal value specifies the rate at which the value and time pairs will be output. A value of 1.0 traverses the list forward at normal speed. A playback rate of -1 traverses the list backwards (i.e. in reverse). A signal value of .5 traverses the linked list at half the normal speed (effectively doubling the delay time values). The value of the input signal is sampled once per input vector. Therefore, any periodic frequency modulation with a period which is greater than the current sample rate/(2*vector_size) will alias. |
|
| skip | number-of-skipped-indices and transition-time [list] |
In left inlet: The word , followed by a positive or negative number, will skip the specified number of indices in the zigzag~ object's linked list. Positive number values skip forward, and negative values skip backward. An optional integer can be used to specify the time over which the transition to the next or previous value will occur (the default value is ). |
| speed | output-rate-coefficient [float] |
In left inlet: The word , followed by a positive or negative floating-point number, specifies the rate at which the value and time pairs will be output. The message traverses the list forward at normal speed, traverses the list backwards, traverses the linked list at half the normal speed (effectively doubling the delay time values). |
| start | starting-position-index [float] |
In left inlet: The word , followed by an which specifies a position (where 0 is the first element), sets the point at which the zigzag~ object begins its output when triggered by a . |
| ramptime | transition-time (milliseconds) [float] |
In left inlet: The word , followed by a number, sets the ramp time, in milliseconds, at which the output signal will arrive at the target value. |
