Examples
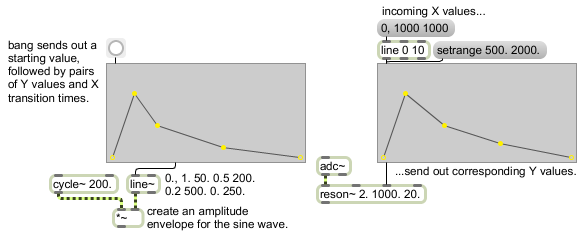
Send line segment information to line~ or look up (and interpolate) individual Y values
Graphical breakpoint function editor
| bang | Triggers a list output of the current breakpoints from the middle-left outlet formatted for use by the line~ object. As an example, if the function contained breakpoints at X = 1, Y = 0; X = 10, Y = 1; and X = 20, Y = 0, the output would be . If the optional output mode is enabled, the output would be . If there are any sustain points in the function, outputs a list of all the points up to the sustain point. Additional points in the function, up to a subsequent sustain point or the end point, whichever applies, can be output by sending the next message. See the description of the and messages for additional information. |
|
| int | x-value [int] |
The value is taken as an X value and outputs a corresponding Y value out the left outlet. The Y value is produced by linear floating-point interpolation of the function. If the X value lies outside the first or last breakpoint, the Y value is . |
| float | x-value [float] |
The value is taken as an X value and outputs a corresponding Y value out the left outlet. The Y value is produced by linear floating-point interpolation of the function. If the X value lies outside the first or last breakpoint, the Y value is . |
| list | x-and-y-values [list] |
If the list contains two values, a new point is added to the function. The first value is X, the second is Y. If the list contains three values, an existing point in the function is modified. The first value is the index (starting at 0) of a breakpoint to modify, the second is the new X value for the breakpoint, and the third is the new Y value for the breakpoint. (If the index number in the list refers to a breakpoint that does not exist, the message is ignored.) |
| clear | breakpoint-indices [list] |
The word by itself erases all existing breakpoints. The word can also be followed by one or more breakpoint indices (starting at 0) to clear selected breakpoints. |
| clearfix | The word clears all fix states (sets them to 0). | |
| clearsustain | The word clears all sustain states (sets them to 0). | |
| dump | receive-name [symbol] |
Outputs a series of two-item lists, containing the X and Y values for each of the breakpoints, out the function object's middle-right outlet. An optional symbol argument can be used to specify a receive objects as a destination. |
| fix | point-index and modify-flag (0 or 1) [list] |
The word , followed by a number specifying the index of a point and 0 or 1, prevents the user from changing the point if the second number is 1, and allows the user to change the point if the second number is 0. By default, points are moveable unless clickmove 0 has been sent to disable moving of all points. |
| getfix | point-indices [list] |
The word . with no arguments, will cause the function object to send a list all fix points out the object's middle-right outlet. If an index is provided as an argument, the fix state for that point will be output. |
| getsustain | point-indices [list] |
The word . with no arguments, will cause the function object to send a list all sustain points out the object's middle-right outlet. If an index is provided as an argument, the sustain state for that point will be output. |
| listdump | receive-name [symbol] |
Outputs a single list which contains all X and Y values for each of the breakpoints out the function object's middle-right outlet.An optional symbol argument can be used to specify a receive objects as a destination. |
| next | The message continues a list output from the sustain point where the output of the last bang or next message ended. For instance, if the function contained breakpoints at (a) X = 1, Y = 0; (b) X = 10, Y = 1; and (c) X = 20, Y = 0, and point b was a sustain point, a message would output and a subsequent message would output After a message reaches the end point, a subsequent message is equivalent to a message. is also equivalent to a when no has been sent that reached a sustain point, or when a function contains no sustain points. | |
| (mouse) | You can use the mouse to draw points in a line segment function; the finished function can then be sent to a line~ object for use as a control signal in MSP. Clicking on empty space in the function adds a breakpoint, which you can begin to move immediately by dragging (unless function has been sent the message). Clicking on a breakpoint allows you to move the breakpoint by dragging (unless function has been sent the message). The X and Y values of the breakpoint are displayed in the upper part of the object’s box. Shift-clicking on a breakpoint deletes that point from the function. Command-clicking on Macintosh or Control-clicking on Windows on a breakpoint toggles the sustain property of the point. Sustain points are outlined in white. Whenever an editing operation with the mouse is completed, a bang is sent out the right outlet. Points with a Y value of 0 are outlined circles; other points are solid. This allows you to see at a glance whether a function starts or ends at Y = 0. |
|
| nth | index [int] |
The word , followed by a number, uses the number as the index (starting at 0) of a breakpoint, and outputs the Y value of the breakpoint out the left outlet. If no breakpoint with the specified index exists, no output occurs. |
| set | x-y-coordinate-pairs [list] |
Given the number of points already defined within function 's graphic editor, a corresponding list of x-y-coordinate pairs will set the position of each point. |
| setdomain | x-maximum [float] |
The word , followed by a or value, sets the maximum displayed X value, then modifies the X values of all breakpoints so that they remain in the same place given the new domain. |
| setrange |
y-minimum [float] y-maximum [float] |
The word , followed by two or values, sets the minimum and maximum display range for Y values, then modifies the Y values of all breakpoints so that they remain in the same place given the new range. |
| sustain |
point-index [int] sustain-flag (0 or 1) [int] |
The word , followed by number specifying the index of a point and zero or one, turns that point into a sustain point if the second number is 1, or into a regular point if the second number is 0. By default, points are regular (non-sustain). The behavior of sustain points is discussed in the description of the message above. Command-clicking on Macintosh or Control-clicking on Windows also toggle the sustain property of a point. |
| Name | Type | g/s | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| autosustain | int def.:0 |
Toggles setting the sustain point to the one before last point. This feature requires that there are more than two points in the current function. The default is 0 (off). | |
| bgcolor | float | Sets the display color for the background in RGBA format. | |
| bordercolor | float | Sets the display color for the function object's border in RGBA format. | |
| clickadd | int def.:1 |
Toggles a user's ability to create new breakpoints by clicking and dragging with the mouse. This feature is enabled by default. | |
| clickmove | int def.:1 |
Toggles a user's ability to move existing breakpoints by dragging them with the mouse. This feature is enabled by default. | |
| clicksustain | int def.:1 |
Toggles a user's ability to specify a sustain point by clicking with the mouse. This feature is enabled by default. | |
| domain | float def.:1000. |
Sets the maximum displayed X value. | |
| legend | int def.:1 |
Toggles the numerical display (legend) of the object, displayed when a point is highlighted or updated. | |
| linecolor | float | Sets the display color for lines in RGBA format. | |
| outputmode | int def.:0 |
Sets the object's output mode. 0 : When the object receives a , it outputs a list of the current breakpoints formatted for use by the object. 1 : When the object receives a , it sends its values in single list in which the first Y value is followed by a 0, followed by any additional Y values and associated times. |
|
| pointcolor | float | Sets the color for points in the display in RGBA format. | |
| range | float def.:0. 1. |
Sets the minimum and maximum display ranges for Y values. | |
| sustaincolor | float | Sets the display color for indicating sustain in RGBA format. | |
| textcolor | float | Sets the display color for text in RGBA format. | |
| zoom_x | float def.:0. 1. |
Sets the horizontal zoom for the function object's display. Zoom values are set using a pair of floating point values in the range 0.0 - 1.0. | |
| zoom_y | float def.:0. 1. |
Sets the vertical zoom for the function object's display. Zoom values are set using a pair of floating point values in the range 0.0 - 1.0. |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Color | Choosing the Color... menu item from the Object menu when the object is selected opens a color picker, permitting adjustment to the appearance of the function object. |

| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| line | Output numbers in a ramp from one value to another |