Examples
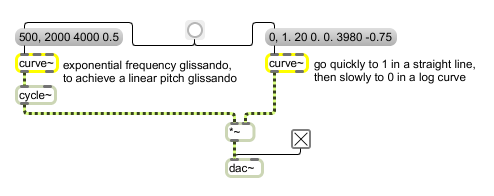
Curved ramps used as control signals for frequency and amplitude
Exponential ramp generator
| Name | Type | Opt | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| initial-value and curve-parameter (floats or ints) | list | opt | The first argument sets an initial value for the signal output. The second argument sets the initial curve parameter. The default values for the initial signal output and curve parameter are 0. |
| int | target-value [int] |
In left inlet: The number is the target value, to be arrived at in the time specified by the number in the middle inlet. If no time has been specified since the last target value, the time is considered to be 0 and the output signal jumps immediately to the target value (ints are converted to floats). |
| float | target-value [float] |
In left inlet: The number is the target value, to be arrived at in the time specified by the number in the middle inlet. If no time has been specified since the last target value, the time is considered to be 0 and the output signal jumps immediately to the target value. |
| list | target-value ramp-time (milliseconds) and curve-parameter (between -1 and 1) [list] |
In left inlet: The first number specifies a target value; the second number specifies an amount of time, in milliseconds, to arrive at that value; and the optional third number specifies a curve parameter, for which values from 0 to 1 produce an exponential curve and values from -1 to 0 produce a logarithmic curve. The closer to 0 the curve parameter is, the more the curve resembles a straight line, and the farther away the parameter is from 0, the more the curve resembles a step. In the specified amount of time, curve~ generates an exponential ramp signal from the currently stored value to the target value. In middle inlet: A list may be used to specify time in one of the Max time formats. |
| anything | object-parameters [list] |
Equivalent to . |
| factor | non-linearizing-factor [float] |
The word followed by a float will adjust the non-linear shaping parameters of curve~. |
| pause | In left inlet: Pauses the internal exponential ramp but does not change the target value nor clear pending target-time-parameter triples. curve~ will continue outputting whatever value was its current value when the message was received, until either it receives a message or until a new ramp is input. | |
| stop | In left inlet: Stops the internal exponential ramp and clears pending target-time parameter triples. curve~ will continue outputting whatever value was its current value when the message was received, resetting its target value to that value. | |
| resume | In left inlet: Resumes the internal exponential ramp and subsequent pending target-time pairs if the curve~ object was paused as a result of the message. |
