Examples
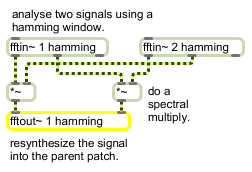
fftout~ converts frequency domain signal pairs into time domain signals and sends them to pfft~
Output for a patcher loaded by pfft~
| Name | Type | Opt | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| outlet-assignment | int | Obligatory. Determines the outlet number in the pfft~ which will receive the output of the fftout~ object. Outlet assignments start at 1 for the leftmost outlet of pfft~. Multiple fftout~ objects will typically have different outlet numbers. | |
| window-envelope-function | symbol | opt | Tells fftout~ which window envelope function to use when overlapping fft's on the input signal. The options are (i.e. no window envelope), (the default), and . If the argument is used, then the fftout~ will echo its input signal to its output without performing a Fast Fourier transform. This allows you to output raw control signals from the pfft~ to the parent patcher. Note that when the option is used, overlap-adding is still being performed to create the output signal. |
| signal | In left inlet: The real part of a signal that will be inverse-transformed back into the time domain. In right inlet: The imaginary part of a signal that will be inverse-transformed back into the time domain. Note that the real and imaginary inlets of fftout~ expect only the first half of the spectrum, as output by fftin~. This half-spectrum is called a spectral frame in pfft~ terminology. |

| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| cartopol | Cartesian to Polar coordinate conversion |
| cartopol~ | Signal Cartesian to Polar coordinate conversion |
| fft~ | Fast Fourier transform |
| fftin~ | Input for a patcher loaded by pfft~ |
| fftinfo~ | Report information about a patcher loaded by pfft~ |
| frameaccum~ | Compute "running phase" of successive phase deviation frames |
| framedelta~ | Compute phase deviation between successive FFT frames |
| ifft~ | Inverse fast Fourier transform |
| out | Message output for a patcher loaded by poly~ or pfft~ |
| pfft~ | Spectral processing manager for patchers |
| poltocar | Polar to Cartesian coordinate conversion |
| poltocar~ | Signal Polar to Cartesian coordinate conversion |
| vectral~ | Vector-based envelope follower |
| MSP Tutorial 25: Using the FFT | MSP Tutorial 25: Using the FFT |
| MSP Tutorial 26: Frequency Domain Signal Processing with pfft~ | MSP Tutorial 26: Frequency Domain Signal Processing with pfft~ |