Examples
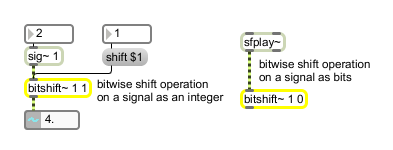
Bit shifting for floating point signals
| Name | Type | Opt | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| number-of-bits/direction-of-shift | int | opt | Sets the number of bits to be shifted on the incoming floating-point signal. Positive shift values correspond to left shifting that number of bits, negative shift values correspond to right shifting that number of bits. |
| operational-mode (0 or 1) | int | opt | Specifies whether the floating signal or floating-point value will be processed as a raw 32-bit floating-point value or converted to an integer value for bit shifting. The modes of operation are: |
| Mode: | Description: | ||
| 0 | int | Treat floating-point signal input as a raw 32-bit value (default). | |
| 1 | int | Convert the floating-point signal input to an integer value. |
| int | operational-mode (0 or 1) [int] |
Sets the operational mode of the bitshift~ object as described by the message. |
| float | operational-mode (0 or 1) [float] |
Performs the same function as . |
| mode | operational-mode (0 or 1) [int] |
In left inlet: The word , followed by a zero or one, specifies whether the floating signal or floating-point value will be processed as a raw 32-bit floating-point value or converted to an integer value for bit shifting. The modes of operation are: Mode Descriptions: 0 - Treat floating-point signal input as a raw 32-bit value (default). 1 - Convert the floating-point signal input to an integer value. Note: If you convert the floating-point signal input to an int and then convert it back, the resulting floating-point value will retain only 24 bits of integer resolution. |
| shift | number-of-bits/direction-of-shift [int] |
In left inlet: The word , followed by a positive or negative number, specifies the number of bits to be shifted on the incoming floating-point signal. Positive number values correspond to left shifting that number of bits (i.e., Left shifting a number n places is the same as dividing it by 2n). Negative numbers correspond to right shifting that number of bits (i.e., Right shifting a number n places is the same as dividing it by 2n). |
| signal | The bitshift~ object performs bit shifting on a floating-point signal as either raw 32-bit data or as an integer value. Floating-point signal bit values are expressed in the following form: <1 sign bit> <8 exponent bits> <23 mantissa bits> |
