Description
Exposes the Javascript language and some Max specific extensions. The js object can be instantiated with a javascript filename or with numerical arguments to specify the number of outlets and inlets respectively. The default number of outlets and inlets are both 1.
Examples
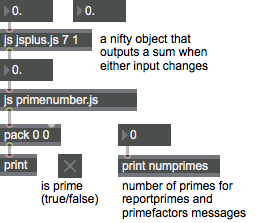
Discussion
Note that this implementation does not include the traditional web browser specific extensions that are often associated with Javascript.
Arguments
filename [symbol]
Specifies the name of a text file to be used as the Javascript source. If no argument is specified, it will not initially have any Javascript associated with it. You can still open a text window and edit and save the Javascript source, but unless you recreate the object with the saved source filename as an argument, the file will not be used when a patch containing the js object is loaded.
inlets-outlets [list]
If no filename is present as an argument, the number of inlets and outlets is specified. If one int argument is present, the number of desired outlets is specified. If two int arguments are present, the first number specifies the number of outlets and the second number specifies the number of inlets.
jsarguments [list]
Following the optional filename or number of outlets and inlets, any symbols or numbers can be entered that will be assigned to the Javascript variable jsarguments. jsarguments[0] is the filename entered, and jsarguments[1] is the first typed-in argument following the filename. The Javascript expression jsarguments.length will be one more than the number of typed-in arguments
Attributes
parameter_enable [int]
Enables use of this object with Max for Live Parameters.
Common Box Attributes
annotation [symbol]
Sets the text that will be displayed in the Clue window when the user moves the mouse over the object.
background [int] (default: 0)
Adds or removes the object from the patcher's background layer. adds the object to the background layer, removes it. Objects in the background layer are shown behind all objects in the default foreground layer.
color [4 floats]
Sets the color for the object box outline.
fontface [int]
Sets the type style used by the object. The options are:
plain
bold
italic
bold italic
Possible values:
0 = 'regular'
1 = 'bold'
2 = 'italic'
3 = 'bold italic'
fontname [symbol]
Sets the object's font.
fontsize [float]
Sets the object's font size (in points).
Possible values:
'8'
'9'
'10'
'11'
'12'
'13'
'14'
'16'
'18'
'20'
'24'
'30'
'36'
'48'
'64'
'72'
hidden [int] (default: 0)
Toggles whether an object is hidden when the patcher is locked.
hint [symbol]
Sets the text that will be displayed in as a pop-up hint when the user moves the mouse over the object in a locked patcher.
ignoreclick [int] (default: 0)
Toggles whether an object ignores mouse clicks in a locked patcher.
patching_rect [4 floats] (default: 0. 0. 100. 0.)
Sets the position and size of the object in the patcher window.
position [2 floats]
Sets the object's x and y position in both patching and presentation modes (if the object belongs to its patcher's presentation), leaving its size unchanged.
presentation [int] (default: 0)
Sets whether an object belongs to the patcher's presentation.
presentation_rect [4 floats] (default: 0. 0. 0. 0.)
Sets the x and y position and width and height of the object in the patcher's presentation, leaving its patching position unchanged.
rect [4 floats]
Sets the x and y position and width and height of the object in both patching and presentation modes (if the object belongs to its patcher's presentation).
size [2 floats]
Sets the object's width and height in both patching and presentation modes (if the object belongs to its patcher's presentation), leaving its position unchanged.
textcolor [float]
Sets the color for the object's text in RGBA format.
textjustification [int]
Text Justification
Possible values:
0 = 'left'
1 = 'center'
2 = 'right'
varname [symbol]
Sets the patcher's scripting name, which can be used to address the object by name in pattr, scripting messages to thispatcher, and the js object.
Parameter Attributes
Order
Sets the order of recall of this parameter. Lower numbers are recalled first. The order of recall of parameters with the same order number is undefined.
Parameter Mode Enable
Parameter Mode Enable (not available from Parameters window)
Link to Scripting Name
When checked, the Scripting Name is linked to the Long Name attribute.
Long Name
The long name of the parameter. This name must be unique per patcher hierarchy.
Short Name
Sets the short name for the object's visual display. The maximum length varies according to letter width, but is generally in a range of 5 to 7 characters.
Type
Specifies the data type. The data types used in Max for Live are:
Float
Int
Enum (enumerated list)
Blob
Note: By convention, the Live application uses floating point numbers for its calculations; the native integer representation is limited to a range of 0-255 (similar to the char data type used in Jitter). When working with Live UI objects whose integer values are likely to be outside of the 0-255 range, the Type attribute should be set to Float, and the Unit Style attribute should be set to Int.
Range/Enum
When used with an integer or floating point data type, this field is used to specify the minimum and maximum values of the parameter.
When used with an enumerated list (Enum) data type, this field contains a space-delimited list of the enumerated values (if list items contain a space or special characters, the name should be enclosed in double quotes).
Modulation Mode
Sets the Modulation Mode used by the Live application. The modulation modes are:
None
Unipolar
Bipolar
Additive
Absolute
Modulation Range
This parameter is only used with the Absolute modulation mode. It specifies defines the range of values used.
Initial Enable
When checked (set to 1), the UI object can store an initialization value. The value is set using the Initial attribute (see below).
Initial
Sets the initial value to be stored and used when the Initial Enable attribute is checked.
Unit Style
Sets the unit style to be used when displaying values. The unit style values are: Int: displays integer values
Float: displays floating point values
Time: displays time values in milliseconds (ms)
Hertz: displays frequency values (Hz/kHz).
deciBel: displays loudness (dB)
%: Percentage
Pan: displays Left and Right values
Semitones: displays steps (st)
MIDI: displays pitch corresponding to the MIDI note number
Custom: displays custom data type
Native: defaults to floating point values
Custom Units
Sets the units to be used with the 'Custom' unit style (see "Unit Style", above). Custom unit strings may be simple symbols (e.g. "Harmonic(s)"), in which case the parameter's value will be displayed in its 'Native' display mode, followed by the symbol (e.g. "12 Harmonic(s)" for an Int-typed parameter or "12.54 Harmonic(s)" for a Float-typed parameter). For additional control over the numerical component displayed, a sprintf-style string may be used (e.g. "%0.2f Bogon(s)", which would display a value such as ".87 Bogons").
Exponent
When set to a value other than 1., the parameter's input and output values will be exponentially scaled according to the factor entered in this column.
Steps
The number of steps available between the minimum and maximum values of a parameter. For instance, if the parameter has a range from 0.-64., with Steps set to 4, the user can only set the parameter to 0, 21.33, 42.66 and 64.
Parameter Visibility
For automatable parameters (Int, Float, Enum), 'Stored Only' disables automation, although parameter values are stored in presets. 'Hidden' causes the parameter's value to be ignored when storing and recalling data. Non-automatable parameters (Blob) are 'Stored Only' by default, and can be set to 'Hidden', if desired.
Update Limit (ms)
Speed limits values triggered by automation.
Defer Automation Output
Defers values triggered by automation.
Messages
bang
int
Arguments
float
Arguments
list
Arguments
anything
Arguments
autowatch
Arguments
compile
Arguments
delprop
Arguments
editfontsize
Arguments
getprop
Arguments
loadbang
open
setprop
Arguments
values [list]
statemessage
Arguments
wclose
methodnote
Output
See Also
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Online Resources | Online Resources |
| Lua in Max | Lua in Max |
| JavaScript Usage | JavaScript Usage |
| jstrigger | Execute Javascript instructions sequentially |
| jsui | Javascript user interfaces and graphics |
| mxj | Execute Java in Max |
| Max JS Tutorial 1: Basic JavaScript | Max JS Tutorial 1: Basic JavaScript |
| Max JS Tutorial 2: JavaScript Scripting | Max JS Tutorial 2: JavaScript Scripting |
| Max JS Tutorial 3: JavaScript Tasks, Arguments, and Globals | Max JS Tutorial 3: JavaScript Tasks, Arguments, and Globals |
| Tutorial 45: Introduction to using Jitter within JavaScript | Tutorial 45: Introduction to using Jitter within JavaScript |
| Tutorial 46: Manipulating Matrix Data using JavaScript | Tutorial 46: Manipulating Matrix Data using JavaScript |
| Tutorial 47: Using Jitter Object Callbacks in JavaScript | Tutorial 47: Using Jitter Object Callbacks in JavaScript |