Examples
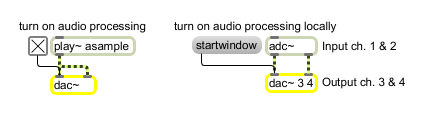
Switch audio on and off send signal to the audio outputs
Audio output and on/off
| Name | Type | Opt | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| number-of-output-channels | int | opt | You can create a dac~ object that uses one or more audio output channel numbers between 1 and 512. These numbers refer to logical channels and can be dynamically reassigned to physical device channels of a particular driver using either the DSP Status window, its I/O Mappings subwindow, or an adstatus object with an output keyword argument.Arguments, If the computer's built-in audio hardware is being used, there will be two input channels available. Other audio drivers and/or devices may have more than two channels. If no argument is typed in, dac~ will have two inlets, for input channels 1 and 2. |
| int | stop/start-flag (0 or nonzero) [int] |
A non-zero number is the same as . is the same as . |
| list | output-channel-designations [list] |
A comprised of integers, sets the logical output channels for each signal inlet in order from left to right. |
| (mouse) | Double-clicking on dac~ opens the DSP Status window. | |
| open | Opens the DSP Status window. | |
| set | output-channel-designation [int] |
In any inlet: The word , followed by a number, sets the logical output channel for the signal inlet in which the message was received. For instance, sending to the left inlet of dac~ makes the signal coming in the left inlet output to logical output channel 3. Note that if the audio is on and you use the message to change a dac~ to use logical channels that are not currently in use, no sound will be heard from these channels until the audio is turned off and on again. For example, if you have a dac~ object with arguments 1 2 3 4 and signals are only connected to the two leftmost inlets (for channels 1 and 2), the message will not immediately route the leftmost audio signal to logical channel 3, because it is not currently in use. A method to get around this is to connect a sig~ to each channel of a dac~ you plan on using for a message. At this point, you might as well use a matrix~ or selector~ object to do something similar before the audio signal reaches the dac~. |
| signal | A signal coming into an inlet of dac~ is sent to the audio output channel corresponding to the inlet. The signal must be between -1 and 1 to avoid clipping by the DAC. | |
| start | Turns on audio processing in all loaded patches. | |
| startwindow | Turns on audio processing only in the patch in which this dac~ is located, and in subpatches of that patch. Turns off audio processing in all other patches. | |
| stop | Turns off audio processing in all loaded patches. | |
| wclose | Closes the DSP Status window if it is open. |

| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| adc~ | Audio input and on/off |
| adstatus | Report and control audio driver settings |
| ezadc~ | Audio input and on/off button |
| ezdac~ | Audio output and on/off button |
| MSP: Audio Input and Output | MSP: Audio Input and Output |
| MSP Tutorial 1: Test Tone | MSP Tutorial 1: Test Tone |