Examples
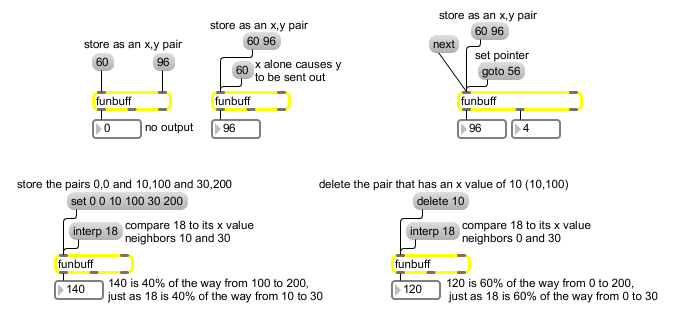
Pairs or lists are stored as x y pairs an x value alone or next sends out a y value... Interpolating between points stored in funbuff
Store x,y pairs of numbers together
| Name | Type | Opt | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| filename | symbol | opt | The argument specifies the name of a file to be read into funbuff when the patch is loaded. Changes to the contents of one funbuff will not affect the contents of another funbuff object with the same name. A file for funbuff can also be created using a text editor window, beginning the text with the word , followed by a list of space-separated numbers which specify alternating x and y values. A funbuff that has been saved as a file can be viewed and edited as text by choosing Open as Text... from the File menu. Numbers in the form of text can be pasted in from other sources such as the editing window of a capture object, or even from another program such as a word processor. |
| bang | In left inlet: Prints information in the Max window concerning the current status of the funbuff object's contents: how many elements it contains, the minimum and maximum x and y values it contains, and its domain and range (the maximum minus the minimum, for the x and y axes respectively). | |
| int | x-value [int] |
In left inlet: The number is the x value of an x,y pair. If a y value has been received in the right inlet, the two numbers are stored together in funbuff. Otherwise, the x value causes the corresponding y value stored in funbuff to be sent out the left outlet. If there is no stored x value which matches the number received, funbuff uses the closest x value which is less than the number received, and sends out the corresponding y value. |
| (inlet1) | y-value [int] |
In right inlet: The number is a y value which will be paired with the next x value received in the left inlet, and stored in funbuff. |
| float | x or y value [float] |
In either inlet: Converted to . |
| clear | Erases the contents of funbuff. | |
| delete |
x-value [int] y-value [int] |
In left inlet: The word , followed by two numbers, looks for such an x,y pair in funbuff, and deletes it if it exists. If is followed by only one number, only the x value is sought, and deleted if it is present. |
| copy | Copies the current selection (made by using the message) into the global funbuff clipboard. The data stored on this clipboard can then be pasted into another funbuff object using the message. | |
| cut | Copies the current selection (made by using the message) into the global funbuff clipboard and deletes it from the funbuff object. The data stored on this clipboard can then be pasted into another funbuff object using the message. | |
| embed | flag (0 or non-zero) [int] |
The word , followed by a non-zero number, causes the funbuff data to be stored inside the patcher. The default setting is not to store the funbuff data inside the patcher. |
| dump | In left inlet: Sends all the stored pairs out the middle and left outlets in immediate succession. The y values are sent out the middle outlet, and the x values are sent out the left outlet, in alternation. The pairs are sent out in ascending order based on the x value. | |
| goto | index [int] |
The word , followed by a number, sets a pointer to the x value (index) specified by the number. A subsequent message will return the y value at the specified x. |
| find | y-value [int] |
The word , followed by a number, will output (out the left outlet) all x values (indexes) whose y value is equal to the number indicated. |
| interp | intermediate-x-value [int] |
In left inlet: The word , followed by a number, uses that number as an x value, measures its position between its two neighboring x values in the funbuff, and then sends--out the left outlet--the y value that holds a corresponding position between the two neighboring y values. If the received number is already the x value in a stored x,y pair, the corresponding y value is sent out. If the received number exceeds the minimum or maximum x values stored in funbuff, the y value that's associated with the minimum or maximum x value is sent out. If the funbuff is empty, is sent out. |
| interptab | input and tablename [list] |
In left inlet: The word , followed by a number and the name of a named table object functions similarly to the message (mentioned above), except that it uses the data in the table as an interpolating function. This allows you to easily perform non-linear interpolation between consecutive values in a funbuff. |
| next | Finds the x value pointed to by the pointer (or, if the pointer points to a number not yet stored as an x value, to the next greater x value), and sends the corresponding y value out the left outlet. Also, funbuff calculates the difference between that x value and the value previously pointed to by the pointer, sends the difference out the middle outlet, and resets the pointer to the next greater x value. | |
| max | Sends the maximum y value currently stored in the funbuff out the left outlet. | |
| min | Sends the minimum y value currently stored in the funbuff out the left outlet. | |
| paste | The word will copy the contents of the global funbuff clipboard into a funbuff object. The contents of the clipboard are set using the , and messages. These messages provide a handy way of copying data between different funbuff objects in any open patchers. | |
| Prints diagnostic information regarding funbuff 's current state in the Max window. | ||
| select | starting-index and range [list] |
In left inlet: The word , followed by an two integers representing a starting index and a range will select a region of the funbuff which can be edited using the , and messages. For example will select the part of a funbuff from index 2 through index 5. |
| set | x-y pair [list] |
In left inlet: The word , followed by one or more space-separated pairs of numbers, stores each pair as x,y pair. |
| read | filename [symbol] |
Calls up the Open Document dialog box so that a file of x,y values can be read into funbuff. If the word is followed by a symbol, Max looks for a file with that name (in the file search path) to load directly into the funbuff. The funbuff file format is described on the next page. |
| undo | The message is used to undo the results of the previous or message. | |
| write | filename [symbol] |
Calls up the standard Save As dialog box, so that the contents of funbuff can be saved as a separate file. If the word is followed by a symbol, the contents of the funbuff are saved immediately in a file, using the symbol as the filename. |

| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| bline | Event-driven multi-segment line object |
| coll | Store and edit a collection of different messages |
| Store x,y pairs of numbers together | |
| itable | A table in a patcher window |
| line | Output numbers in a ramp from one value to another |
| table | Store and graphically edit an array of numbers |