capture~
Description
Use the capture object to collect signal values for signal debugging or investigation. To record signal values, use the record~ or sfrecord~ object.
Examples
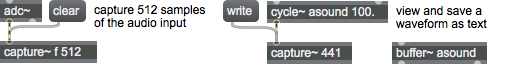
Arguments
behavioral-flag (f) [symbol]
If the first argument is the letter , capture~ stores the first signal samples it receives, and then ignores subsequent samples once its storage buffer is full. If the letter is not present, capture~ stores the most recent signal samples it has received, discarding earlier samples if necessary.
maximum-samples [int]
Limits the number of samples (and thus the length of the excerpt) that can be held by capture~. If no number is typed in, capture~ stores 4096 samples. The maximum possible number of samples is limited only by the amount of memory available to the Max application. A second number argument may be typed in to set the precision (the number of digits to the right of the decimal point) with which samples will be shown in the editing window. When set to mc mode (mc.capture~), the maximum-samples value applies to each channel. Captured values are displayed in sequence by channel number.
signal-vector-indices (up to 10 ints) [list]
A list of up to 10 indices within a signal vector. If no indices present, capture~ records the entire vector.
Attributes
Common Box Attributes
annotation [symbol]
Sets the text that will be displayed in the Clue window when the user moves the mouse over the object.
background [int] (default: 0)
Adds or removes the object from the patcher's background layer. adds the object to the background layer, removes it. Objects in the background layer are shown behind all objects in the default foreground layer.
color [4 floats]
Sets the color for the object box outline.
fontface [int]
Sets the type style used by the object. The options are:
plain
bold
italic
bold italic
Possible values:
0 = 'regular'
1 = 'bold'
2 = 'italic'
3 = 'bold italic'
fontname [symbol]
Sets the object's font.
fontsize [float]
Sets the object's font size (in points).
Possible values:
'8'
'9'
'10'
'11'
'12'
'13'
'14'
'16'
'18'
'20'
'24'
'30'
'36'
'48'
'64'
'72'
hidden [int] (default: 0)
Toggles whether an object is hidden when the patcher is locked.
hint [symbol]
Sets the text that will be displayed in as a pop-up hint when the user moves the mouse over the object in a locked patcher.
ignoreclick [int] (default: 0)
Toggles whether an object ignores mouse clicks in a locked patcher.
jspainterfile [symbol]
JS Painter File
patching_rect [4 floats] (default: 0. 0. 100. 0.)
Sets the position and size of the object in the patcher window.
position [2 floats]
Sets the object's x and y position in both patching and presentation modes (if the object belongs to its patcher's presentation), leaving its size unchanged.
presentation [int] (default: 0)
Sets whether an object belongs to the patcher's presentation.
presentation_rect [4 floats] (default: 0. 0. 0. 0.)
Sets the x and y position and width and height of the object in the patcher's presentation, leaving its patching position unchanged.
rect [4 floats]
Sets the x and y position and width and height of the object in both patching and presentation modes (if the object belongs to its patcher's presentation).
size [2 floats]
Sets the object's width and height in both patching and presentation modes (if the object belongs to its patcher's presentation), leaving its position unchanged.
textcolor [4 floats]
Sets the color for the object's text in RGBA format.
textjustification [int]
Sets the justification for the object's text.
Possible values:
0 = 'left'
1 = 'center'
2 = 'right'
varname [symbol]
Sets the patcher's scripting name, which can be used to address the object by name in pattr, scripting messages to thispatcher, and the js object.
Messages
clear
(mouse)
open
signal
wclose
write
Arguments
Output
(text)
capture~ outputs nothing and has no outlet but the signal which it captures into text can be saved to a file or copied and pasted elsewhere for editing.
See Also
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| scope~ | Visualize an audio signal |
| MSP Analysis Tutorial 1: Signals and Meters | MSP Analysis Tutorial 1: Signals and Meters |
| MSP Analysis Tutorial 3: Using the FFT | MSP Analysis Tutorial 3: Using the FFT |