Arrays
Arrays are a data type in Max. Similar to lists, arrays store multiple items in order. Unlike lists, which are limited to storing numbers and symbols, arrays can store other Max data structures including strings, dictionaries, and other arrays. Similar to dictionaries and strings, arrays are stored in memory by name. Generally, arrays are a more powerful version of lists.
When to Use Arrays
Creating an Array
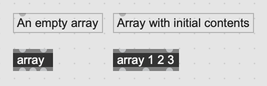
Create an array with the array object. Initialize the contents of the array by including the initial values as object arguments.
Editing Arrays
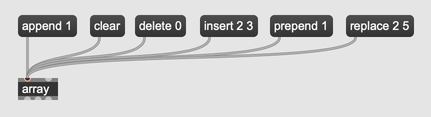
Edit an array in place by using the append, clear, delete, insert, prepend, and replace messages.
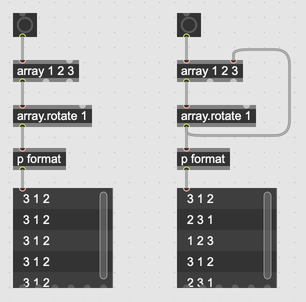
Objects that modify arrays as they pass through them, like array.rotate, don't change the original array, but create a new array with the result of their computation. In this example, the objects on the left always output the same result, but the objects on the right will update the original array with every rotation.
Named Arrays
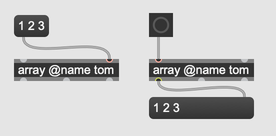
Like dictionaries and strings, arrays always have a unique name. By default, the name will simply be a randomly generated unique identifier. You can also assign a name to an array using the @name attribute.
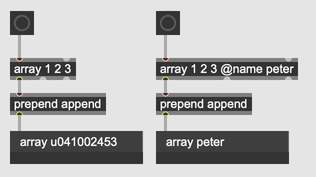
An array is identified by its unique name, so you can access the same array from any array object with the same name.
Converting to and from a List
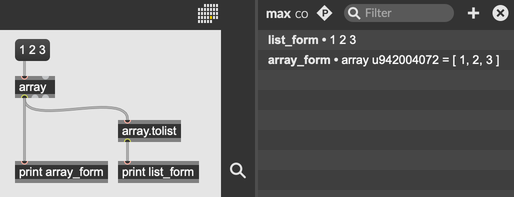
Any list sent to an array object will automatically be converted to an array. When it comes to working with arrays and lists, many objects will use arrays and lists interchangeably. However, in some circumstances, you might need to use a list and not an array. In these cases, you can use the array.tolist object to convert an array into a list.
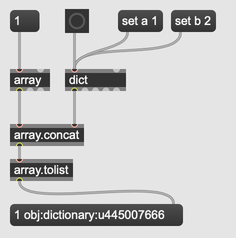
If the array contains structured data, like dictionaries or other arrays, converting to a list will not unpack the contents of any structured data object. Instead, the list will simply contain a symbol representation of the object.
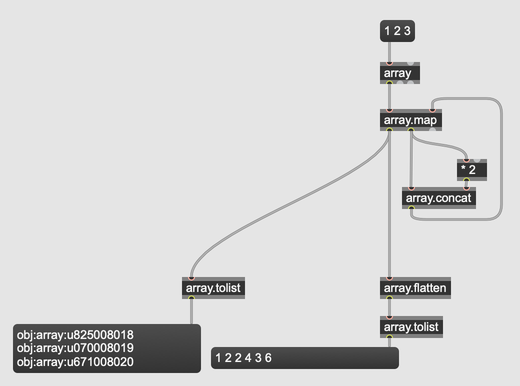
If your array contains only numbers, symbols/strings, and other arrays, you can use the object array.flatten to collect all sub-arrays and their contents into one long array. This can then pass through the array.tolist object to return a simple representation of your array's contents.
Arrays and Dictionaries
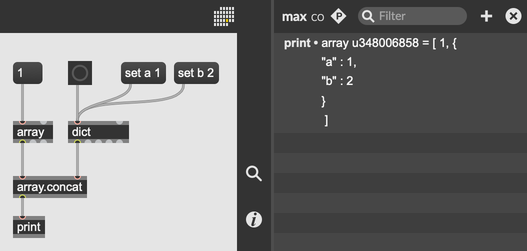
Dictionaries can contain arrays, and arrays can contain dictionaries. Printing an array containing a dictionary will output a JSON representation of the dictionary.
JavaScript
Use the MaxArray class to create a JavaScript reference to a Max Array.
You can give it an initial value by passing a list or Array value to the
constructor. Update the value of the array by calling .set.
var max_arr = new MaxArray(1, 2, "three", 4.0);
max_arr.set(10, 9, "eight", 7.0); // update the array contents
By setting the name property of the MaxArray, you can refer to a Array
defined in the parent patcher.
var max_arr = new MaxArray();
max_arr.name = "frith"; // Now the MaxArray refers to an array named "frith"
max_arr.set(2, 4, "six", 8); // Updates the array in the containing patcher
If you want to manipulate the Array value, call .stringify and JSON.parse to turn
the Max Array into a JavaScript Array. From there, you can use regular JavaScript
array manipulation functions. To convert back, use JSON.stringify and .parse.
var max_arr = new MaxArray();
max_arr.set(2, "3", "four", 6);
var js_arr = JSON.parse(max_arr.stringify()); // retrieve the value as a JS string, convert to Array
post(JSON.stringify(js_arr) + '\n'); // prints "[2, '3', 'four', 6]"
js_arr[1] = 3;
max_arr.parse(JSON.stringify(js_arr));
post(max_arr.stringify() + '\n'); // prints "[2, 3, 'four', 6]"
To send a Max Array out of an outlet defined in JavaScript, send the string "array" followed by the name of the array.
function bang() {
var arr = new MaxArray();
arr.parse("[I, got, a, bang]");
outlet(0, "array", arr.name);
}