Transport
Most DAWs, especially those that organize audio and MIDI into tracks, have some notion of a playhead. When you tell the program to "play", the playhead represents the point in the current song or session at which play will resume. There are usually controls to play, stop, and loop playback, as well as some way to set the tempo and time signature. Max doesn't organize audio and MIDI into tracks and clips, but it does have a transport that you can use to organize events in time.
Accessing the Global Transport
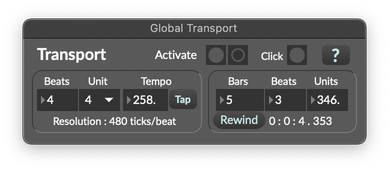
Open the Global Transport by choosing Global Transport from the Extras menu. This will bring up the Global Transport window, which is an interface to Max's shared global transport. All patches in Max can access this transport, and objects that work with the transport can react when the transport starts, stops, changes position, or changes tempo.
Controlling the Transport
From the Global Transport window, you can start and stop the transport by clicking the Activate button at the top of the window. It's also possible to start the global transport from the toolbar of any Max patcher. The play button on the right of the bottom toolbar can start and stop the global transport.
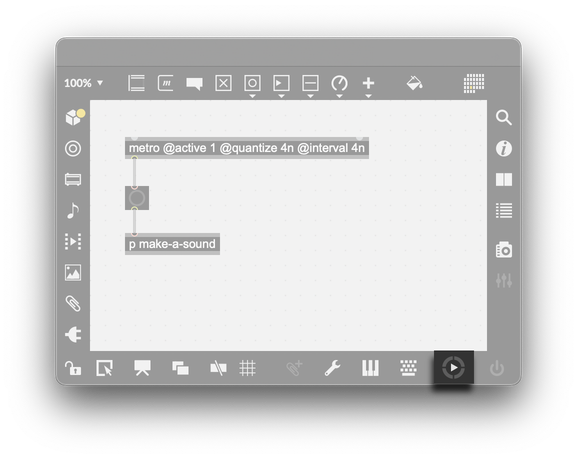
To change the tempo of the global transport from the patcher toolbar, option- or alt-drag up or down on the play button control. The current tempo will be displayed in a caption above the control.
The transport object can also act as an interface to the global transport. This object lets you control all aspects of the transport, including play/pause state, tempo, and time signature, as well as retrieving the current play position.
Named Transports
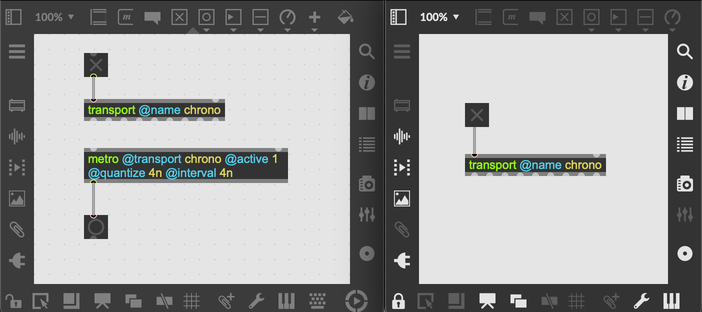
In addition to the global transport, it's also possible to create named transports using the @name attribute of a transport object. All transport objects with the same name essentially act as an interface to the same, shared transport, and this includes transport objects in different Max patches.
The Global Transport has the reserverd name internal. If you send a transport object the message name internal, that object will act as an interface to the global transport.
By default, objects like metro and timepoint refer to the Global Transport. To refer to a particular, named transport, use the @transport attribute of these objects.
Max for Live
In a Max for Live device, the transport object will be bound to Live's transport. You can send the object a bang to get the current state of Live's transport, but you can't control Live's tranport this way. Instead, use the Max for Live API to interface with the Live application link to the relevant doc here. Other named transports—transports not bound to the Live transport—are not supported.
Transport Resolution
The resolution of the transport is always 480 PPQ (reference to the MIDI standard). When it comes to scheduling events, the transport uses the same Scheduler as all other events in Max, and so ultimately the resolution of the Max scheduler determines the resolution of transport events.