Examples
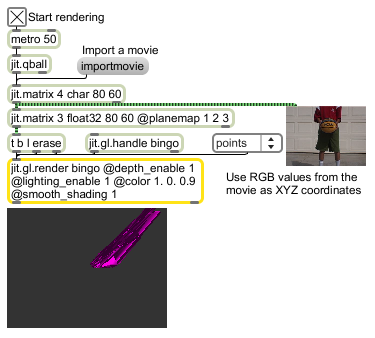
Render Open GL
There are two ways of drawing things with jit.gl.render : creating Jitter OpenGL objects such as the jit.gl.plato object, and sending drawing commands directly to the jit.gl.render object. When you create new jit.gl objects, they appear automatically in the OpenGL scene and are redrawn each time a bang is sent to the jit.gl.render object. This provides an easy way to begin drawing 3D scenes. When you use drawing commands directly to a jit.gl.render object, you must create a patch which sends the desired sequence of drawing messages for each frame. This method of drawing offers lots of flexibility.
The most commonly used drawing command is jit_matrix . Matrices sent using this command are drawn as 2D or 3D geometry, according to the currently set graphics primitive or one set explicitly in the command. Other drawing commands include draw_pixels , which draws the matrix contents as a 2D picture, and test , which draw standard SMPTE color bars.
OpenGL is a standard for 3D drawing based on a complex virtual machine with commands for viewing, lighting, texturing, 2D imaging, and frame buffer control. A full discussion of OpenGL is beyond the scope of this reference. A valuable starter reference is the OpenGL "Red Book". please see www.opengl.org for more information.
| erase | Overwrites the image buffer with the color and opacity selected by the erase_color attribute. | |
| deletetexture | texture-name [symbol] |
Followed by a texture name, delete the named texture. |
| depth_grab | Copy the depth buffer to a named texture | |
| draw_pixels | Followed by a jit.matrix, draw the matrix data as a 2D image filling the screen. | |
| drawclients | layer [int] |
Draw all automatic clients, optionally with specific layer number. |
| drawswap | Draw all automatic clients, and copy the rendered image to the destination jit.window, jit.pwindow or jit.matrix. | |
| jit_glchunk | For internal use only. | |
| interp | 0/1 [int] |
Toggles interpolation for the currently selected named texture (default = 0) |
| line_loop | Sets the draw primitive to draw the matrix geometry as a loop of lines connecting each vertex and then returning to the first. | |
| line_strip | Sets the draw primitive to draw the matrix geometry as a strip of lines connecting each vertex. | |
| lines | Sets the draw primitive to draw the matrix geometry as unconnected lines between each pair of vertices. | |
| points | Sets the draw primitive to draw the matrix geometry as points. | |
| quad_grid | Sets the draw primitive to draw the matrix geometry as a grid connecting neighboring matrix elements. Each vertex in the matrix is connected to the vertices next to it in the x and y directions. Each square of vertices ((x,y), (x+1,y), (x,y+1),(x+1,y+1)) is then drawn as one quadrilateral. | |
| quad_strip | Sets the draw primitive to draw the matrix geometry as a strip of connected quadrilaterals. | |
| quads | Sets the draw primitive to draw the matrix geometry as unconnected quadrilaterals. | |
| point_sprite | Set point sprites as the render primitive for the object. | |
| polygon | Sets the draw primitive to draw the matrix geometry as vertices of one simple polygon. | |
| test | Draws a set of SMPTE standard color bars to the output. | |
| sendtexture | message [list] |
Sends the internal jit.gl.texture object, currently selected with the method, the corresponding message. |
| swap | Copy the rendered image to the destination jit.window, jit.pwindow or jit.matrix. | |
| updateclients | Update the render list (list of attached jit.gl objects). | |
| usetexture | texture-name [symbol] |
Use the named texture for drawing primitives. |
| to_texture | Copy the previously drawn frame to the named texture. Useful for feedback effects. | |
| tri_fan | Sets the draw primitive to draw the matrix geometry as a fan of connected triangles. | |
| tri_grid | Sets the draw primitive to draw the matrix geometry as a grid connecting neighboring matrix elements. Each vertex in the matrix is connected to the vertices next to it in the x and y directions. Each square of vertices ((x,y), (x+1,y), (x,y+1),(x+1,y+1)) is then drawn as two triangles. | |
| tri_strip | Sets the draw primitive to draw the matrix geometry as a strip of connected triangles. | |
| triangles | Sets the draw primitive to draw the matrix geometry as unconnected triangles. | |
| screentoworld |
x [float] y [float] z [float] |
Converts screen coordinates to world coordinates, output out the dump outlet. The input x and y input coordinates are in pixels, and the input z coordinate is in normalized distance from camera (0.-1.), where 0. is the near clipping plane and 1. is the far clipping plane. |
| worldtoscreen |
x [float] y [float] z [float] |
Converts screen coordinates to world coordinates, output out the dump outlet. The output x and y input coordinates are in pixels, and the output z coordinate is in normalized distance from camera (0.-1.), where 0. is the near clipping plane and 1. is the far clipping plane. |
| Name | Type | g/s | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| accelerated | int | Toggles enabling hardware-accelerated rendering. | |
| aux_buffers | int | Set the number of auxiliary buffers available | |
| camera | float | The camera position in 3D space (default = 0. 0. 2.) Camera position is specified as a set of floating point numbers that correspond to a camera position with respect to the x, y, and z axes. | |
| copy_texture | symbol | Named texture to copy the framebuffer to. | |
| debug | int | If enabled and jit.gl.render detects lack of support for versions of OpenGL later than 1.2, it will print a summary of the capabilities of the rendering context to the Max window for diagnosis. | |
| doublebuffer | int | Toggles double buffering the drawing context (front and back buffers). You may prefer so set double buffering in the jit.window object instead. | |
| draw_buffer | symbol | Sets the drawing buffer. This feature is useful for active stereo drawing. Possible values are: back front left right back_left back_right, front_left front_right front_and_back |
|
| drawto | symbol | Select the drawing destination for output. Must be a named jit.window, jit.pwindow or jit.matrix. | |
| erase_color | float | Color and opacity with which image is overdrawn on receipt of message in the form (default = 0. 0. 0. 1. (opaque black)) All values should be in the range 0.-1. | |
| far_clip | float | The far clipping plane distance in 3D world (default = 100.) | |
| fsaa | int | Enables full-scene anti-aliased drawing. You may prefer so set fsaa in the jit.window object using the attribute. | |
| geom_rows | int | Vertex connection mode (default = 0 (connect along columns)) 0 = connect vertices in 2D geometry matrix along columns 1 = connect vertices in 2D geometry matrix along rows |
|
| lens_angle | float | The lens angle of the OpenGL camera (default = 45.) | |
| light_ambient | float | The color and opacity of the ambient light component in the form (default = 0. 0. 0. 1. (opaque black)) All values should be in the range 0.-1. | |
| light_diffuse | float | The color and opacity of the diffuse light component in the form (default = 1. 1. 1. 1. (opaque white)) All values should be in the range 0.-1. | |
| light_global_ambient | float | The color and opacity of the global ambient light component in the form (default = 0.2 0.2 0.2 1.) All values should be in the range 0.-1. | |
| light_position | float | The position of the light source in XYZ coordinates and the light type (default = 1. 1. 1. 0.) When the last number is 0., t The light is treated as a directional source if 0. is the final number. Otherwise, diffuse and specular lighting calculations are based on the actual location of the light in eye coordinates, and attenuation is enabled. |
|
| light_specular | float | Color and opacity of specular light component (default = 1. 1. 1. 1. (opaque white)) The first three floats in the range 0.-1. specify the RGB components of the specular light color. The fourth float (also in the range 0.-1.) specifies opacity. | |
| lookat | float | 3D position at which the camera is pointed (default = 0. 0. 0.) | |
| near_clip | float | The near clipping plane distance in 3D world (default = 0.1) | |
| point_atten | float | Sets the point attenuation factor for point sprites | |
| point_fade | float | Sets the point fade threshold for point sprites. | |
| primitive | symbol | The current drawing primitive (default = tri_grid) | |
| quality | int | Quality flag when using software renderer (default = 0). (Mac only) Slower than normal SW renderer, but supports larger rendering, shaders, and other advanced features. | |
| shared_context | symbol | The name of a context to share resources (i.e. textures) with. | |
| stereo | int | Sets the rendering context as stereo. You may prefer so set this in the jit.window object | |
| sync | int | Sets the vertical sync of the render context. You may prefer so set this in the jit.window object. | |
| up | float | The 3D vector towards which the top of the camera points (default = 0. 1. 0.) | |
| verbose | int | Toggles printing messages to the Max Window. |

| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| jit.gl.graph | Open GL floating-point data visualization |
| jit.gl.gridshape | Generate simple geometric shapes as a connected grid |
| jit.gl.handle | Use mouse movement to control position/rotation |
| jit.gl.isosurf | Generates a GL based surface extraction |
| jit.gl.mesh | Generates GL geometry from existing data |
| jit.gl.model | Read and draw Wavefront .obj models |
| jit.gl.nurbs | Generate NURBS surface |
| jit.gl.plato | Generate platonic solids |
| jit.gl.shader | Manages a GL shader |
| jit.gl.sketch | GL parallel to lcd |
| jit.gl.slab | Performs a GL accelerated grid-based evaluation |
| jit.gl.text2d | Write bitmap text |
| jit.gl.text3d | Write vector text |
| jit.gl.texture | Manages a GL texture |
| jit.gl.videoplane | GL accelerated video plane |
| jit.gl.volume | Creates a GL accelerated volume vizualization |
| Tutorial 30: Drawing 3D text | Tutorial 30: Drawing 3D text |
| Tutorial 31: Rendering Destinations | Tutorial 31: Rendering Destinations |
| Tutorial 32: Camera View | Tutorial 32: Camera View |
| Tutorial 33: Polygon Modes, Colors and Blending | Tutorial 33: Polygon Modes, Colors and Blending |
| Tutorial 34: Using Textures | Tutorial 34: Using Textures |
| Tutorial 35: Lighting and Fog | Tutorial 35: Lighting and Fog |
| Tutorial 37: Geometry Under the Hood | Tutorial 37: Geometry Under the Hood |
| Tutorial 47: Using Jitter Object Callbacks in JavaScript | Tutorial 47: Using Jitter Object Callbacks in JavaScript |